Disavow Links, Every content marketer wishes to have high-quality inbound links to their blog. Those backlinks can offer your SEO efforts a tremendous boost and help you climb the SERPs faster.
But what about the poor-quality backlinks? You know, the ones from spammy websites with low-quality content and low domain authority. Google created a tool for disavowing links to assist you in removing these harmful connections.
This tutorial was intended to help you understand this functionality. We’ll explain how Google’s link disavow tool works, provide a list of links to consider disavowing, and provide expert advice on the process.
What is the purpose of Google’s Disavow Links Tool?
Google’s disavow links tool, introduced in 2012, allows you to request that Google ignore certain backlinks. The disavow links tool’s objective is to essentially clean up your backlink profile and remove any spammy, low-quality backlinks that may be lowering your site’s search engine rating.
Disavowing links is often regarded as the last option that should not be used on a frequent basis. That’s because there’s always the possibility that Google will penalize you if you disavow decent backlinks or ones that weren’t causing any SEO issues. Most small to medium-sized firms will not use this product because they do not deal with huge and complex connection networks.
That being said, if you’ve received a manual action message in Google Search Console that looks like the one below, it’s time to think about disavowing links.
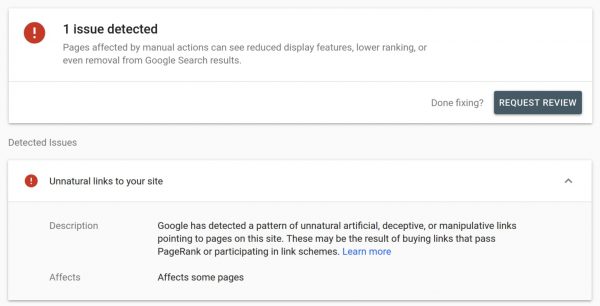
This Google warning suggests that there may be harmful links, spammy links, or unnatural links to your site. They could be related to link schemes, which are manipulation strategies used to help you rank higher. These can involve buying and selling links, high-volume link trading, and using systems to bring links to your site automatically.
To avoid receiving this notice, examine your backlinks on a frequent basis and keep an eye out for suspicious links that could cause negative SEO difficulties and drive Google’s algorithm to reduce your rating. Read through Google’s webmaster quality standards to gain a better picture of what they want in terms of website quality.
If you see this notification, you should disavow links to prevent being penalized. To do so, go to Google Search Console, choose your website, and add a file containing the links you wish to disavow. After you’ve completed those procedures, Google will examine the links and re-crawl your site, which often takes a few weeks.
After you’ve resolved the potential manual penalty and removed the backlinks, contact Google Search Console to request a reconsideration request – a follow-up assessment of your site to ensure you’ve disavowed any links that were causing problems. You can also request that Google recrawl your URLs so that new links and bad link removal are recognized.
Check the “Links to Your Site” area of Google Search Console to gain a better knowledge of your backlink profile. It displays which websites link to your content:
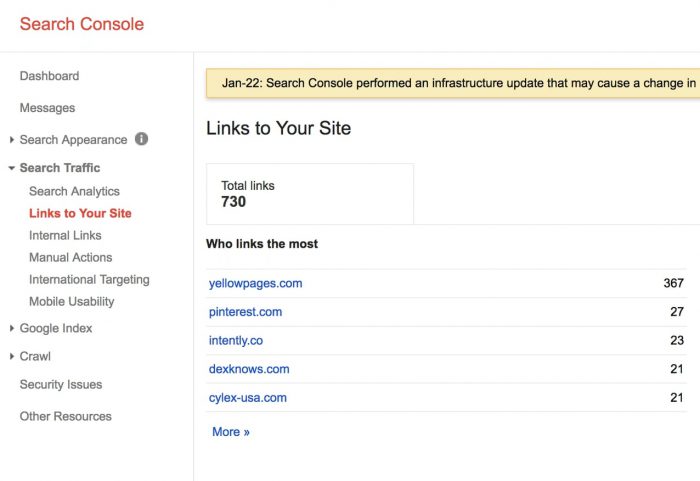 This data might assist you in identifying spammy sites that are linking to your material. You can export this list and filter through the file to locate all dubious connections in your own disavow list, then carefully investigate each one. This informal backlink audit will assist you in identifying all dodgy backlinks that may result in a Google algorithmic penalty.
This data might assist you in identifying spammy sites that are linking to your material. You can export this list and filter through the file to locate all dubious connections in your own disavow list, then carefully investigate each one. This informal backlink audit will assist you in identifying all dodgy backlinks that may result in a Google algorithmic penalty.
5 Link Types to Consider Disavow Links
Bad backlinks come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The following are a few examples of the most typical categories to be on the lookout for. While this list does not include all of the sorts of connections you should disavow, it is an excellent place to start.
Spam Links in Comments and Forums
Users referring back to similar information in comments or forums are not necessarily frowned upon by Google. However, it is difficult for webmasters who use forums to boost their backlink profiles. If you go to trustworthy websites and try to flood their comment or forum areas with links back to your website with no context, Google may consider it spam and may penalize your site.
Domain Links That Have Expired
Even if you have links from reputable websites, they are useless if they are inactive. Maybe these were formerly links from websites you’d never dreamed of disavowing. When they expire, all Google sees is a violation of their webmaster quality criteria and can penalize you for it.
Links to Low-Quality and Spammy Websites
Spammy sites with a high number of outbound links, or sites that appear to be hacked, should be avoided. This could also indicate that your site is the target of a negative SEO effort. If you do not disavow these links, keep an eye on the manual actions area of your Search Console dashboard to ensure that no more action is required.
Paid Links
Paid links are just hyperlinks to your website that you pay for. While they are famously tough to catch, there are methods for detecting them. If you see the term “sponsored post” on an article with do-follow links, that’s a paid link. Paid links, on the other hand, can be more covert and appear in the form of do-follow links with exact match anchor text. That doesn’t always indicate it’s a paid link, so make sure the site isn’t full of spam or low-quality content.
Links to Private Blog Networks
Private blog networks (PBNs) are vast collections of blogs and sites that are all maintained by the same person in order to generate backlinks amongst them and get their content to rank higher on Google. They were popular a few years ago, but they are no longer considered a viable white hat SEO approach. In 2014, Google abandoned PBNs and began the process of de-indexing them entirely. If numerous sites have very similar backlink profiles or if one site is continuously being linked to, you can recognize them. If you notice any PBN links to your site, you should consider disavowing them.
3 SEO Experts’ Best Practices for Disavow Links
If you find a spammy link pointing to your site, don’t immediately disavow it. According to Matt Cutts, a former Google distinguished engineer, the first approach is to contact someone at the website responsible for the backlink and request that it be deleted personally.
While some people may react to your request, there is a good probability you will not receive a response from many of these websites. If this occurs, Alex Panagis, CEO of SEO and marketing firm ScaleMath, advises taking a proactive or reactive approach to disavowing links.
A proactive method comprises analyzing your backlinks on a regular basis to guarantee they are not originating from spammy, low-quality web pages. To mitigate any bad SEO impact, a reactive method is to use Google’s disavow links tool.
According to Panagis, the reactive method is more typical for disavowing links. This is due to the fact that Google is already extremely adept at comprehending links. There’s no urgent need to aggressively seek out those poor backlinks unless you’re afflicted by a big amount of spam that you detect before Google.
However, Panagis’ proactive approach is also a possibility.
“Update your disavow file as you go to lessen the danger of your site ever being harmed, so you never have to worry about the day when your site is suddenly damaged,” Panagis explains.
According to Jason Berkowitz, CEO of inbound digital marketing agency Break the Web, you must also be exceedingly cautious when disavowing. He claims that disavowing good backlinks, even if done inadvertently, might have a negative impact on your search ranking. He only advises disavowing links if the backlink is likely to have a negative impact, such as a decline in traffic or a manual penalty.
This sentiment is shared by Panagis.
“If you have a high-authority domain that organically gets a lot of links when the site is released, as long as the link profile is diverse and the majority isn’t spammed,” explains Panagis.
Explore more : PPC and SEO, Nofollow vs. Dofollow, Site architecture, SEO Ranking Factors