Do you have clients in more than one country? Do any of your consumer segments speak more than one language? If you responded yes to either of those questions, then international SEO is something you should look into. With these international SEO strategies, you can generate more visitors, expand your global presence, and better serve your consumers by using best practices on your website.
What Exactly Is International SEO?
International SEO is the process of improving your search visibility for visitors in other nations or who speak different languages. You can target information to viewers all across the world by using geo-targeting, hreflang tags, and other localization signals.
How international SEO works: Google makes an effort to match search results to the searcher’s language and location. Special signals you include on your website let Google and other search engines recognize whether your site contains content that is appropriate for someone in a specific country or looking in a specific language.
Here are four critical stages for integrating international SEO into your website.
Step 1: Determine the type of international content you will offer
Do you want to improve search results by language, geography, or both?
Some websites opt to emphasize language, such as Facebook’s home page, which allows visitors to choose their preferred language.
Air Canada employs a pop-up to allow some users to choose their language and nation and then directs them to a specific URL based on their pick.
You can also target content by country AND language like eBay does with various markets in the local languages of 23 different nations. Boden, a British apparel company, tailors its content to customers in the United Kingdom, the United States, Germany, France, Australia, and other countries.
As you can see, the spectrum of content extends from just translating your English information into additional languages to generating customized experiences, such as eBay. Once you’ve decided what international material you’ll offer, you’ll need to figure out how to arrange your website for international SEO.
Don’t know which countries to target for international SEO? Identifying countries that are providing a lot of connections or traffic to your site is one element to consider. To find out which nations are driving traffic to your website, use Alexa’s free Site Overview tool. If you notice a lot of traffic from a country that you aren’t optimized for, you should think about optimizing for such countries. You may also use Google Analytics’ Language report to see which languages your users speak.
Step 2: Create a Global SEO-Friendly URL Structure
Google uses your URL structure to determine which of your pages to show to searchers in different countries. This is a type of geo-targeting that focuses on location. We’ll teach you how to utilize the hreflang tag in a moment to further target for language.
Most companies either create a new website for each target country or add a subdirectory structure to their existing website. The technique you choose will be heavily influenced by the resources you have available to devote to its creation and upkeep. Let’s go over the benefits and drawbacks of each URL structure for international SEO.
Explore more : PPC and SEO, Nofollow vs. Dofollow, Site architecture, SEO Ranking Factors
On Your Main Website, Create a Subdirectory for Each Country
Create a folder on your website for each target nation labeled with the country’s two-letter ISO code to build up a subdirectory structure. To signal material aimed at people in Spain, for example, your subfolder would look like this: website.com/es.
Advantages of employing subdirectories: A subdirectory structure is simple to create and maintain. It is simple and inexpensive to add subdirectories to your website. It just requires one website domain, and the authority you establish for that domain applies to the entire site. Some believe that this alternative has emerged as the clear choice for almost any organization.
Cons: A subdirectory’s worldwide SEO signal is weaker than if you set up a website entirely dedicated to a country.
Best for: A company or organization that wants to service businesses in many countries while keeping all communications on one website.
Companies that employ subdirectories for their international websites include:
- For users in the United Kingdom, go to apple.com/uk/.
- Nike (nike.com/za/ for South African users)
- Spotify (spotify.com/ar/ for Argentina users)
Each country has its website
Some businesses decide to create a different website for visitors from each targeted country. This is referred to as a local country code top-level domain (ccTLD). In Spain, a ccTLD for your users would look like this: website.es.
Some codes are “open,” which means they can be used for purposes other than representing the country. For example,.co is the official country code for Columbia, but you’re probably more familiar with it as a synonym for “business” or “corporation.” Some ISO codes have also been established for usage with cities, such as. to for Toronto and. to for Tokyo, in addition to. to for Tonga. The ICANNWiki keeps track of country code top-level domains.
Advantages of utilizing ccTLDs:
For international SEO, dedicating a separate domain with a country code provides the most strong country signal to search engines. It also communicates to website visitors that your company is committed to having a presence in that country.
Cons: Keeping separate web pages for each country might be costly. When it comes to foreign SEO, you’ll also need to establish authority for each website individually.
Best for: Large corporations with extensive resources. Because maintaining many websites is so costly, it’s usually not a smart option for small enterprises. If you’re going after China, there’s an exception. Without the. cn top-level domain, it might be difficult for websites to rank on Baidu, China’s most popular search engine.
Companies that use various websites (ccTLDs) for different countries include:
- Sony (Chinese business website: sony.com.cn/)
- Disney (French shopping site: shopdisney.fr/)
- McDonald’s (mcdonalds.rs/ in Serbia)
Subdomains are a less popular option for international SEO
In principle, you have a third option: create a subdomain on your website for each country. However, the disadvantages exceed the benefits in most cases.
A subdomain’s international SEO signal is weaker than that of a specific country domain. It may also be more difficult to make use of the main domain’s authority for subdomains than for subdirectories. (While Google claims that subdomains and subdirectories are treated similarly for ranking webpages, SEO professionals disagree if this is accurate. Many people claim that pages on a subdomain do not benefit from the parent domain and are instead treated as independent domains by Google, or that subdomain may undermine the authority of the root domain.) You will also have to pay hosting fees for each subdomain.
If the appropriate URL structure for your company does not appear to be obvious, look at rivals in your target country.
Running a Site Comparison for your top ten competitors is one approach to acquire worldwide competitive intelligence using Alexa. You can switch between views for any country in the world by clicking the top right-hand drop-down menu. If your key competitors are receiving a lot of traffic from one of your target nations, you should look into their international SEO strategies for that country.
Before creating your URL structure, make sure you have the correct country code. Also, bear in mind that regardless of the URL structure you use, Google may still offer the erroneous material to searchers on occasion. The hreflang tag can send additional signals to Google to help it determine when to reveal what.
Step 3: Use Hreflang Tags to Target Languages
Hreflang tags are bits of code that are used on websites that include material in various languages. They assist search engines in matching the appropriate language with the searcher. French speakers, for example, will view your French material rather than your English or Italian content.
How does Google determine what language a user prefers? Of course, the terms entered by the searcher are important cues. Google, on the other hand, considers data such as the user’s settings, search history, location, and which Google domain they are using (Google.com vs. Google.de, for example).
When offering translations of your content in subdirectories or subdomains, the hreflang tag comes in handy. While search engines can usually detect the language of a page without the use of hreflang tags, the tags assist keep your different page versions from competing in search results. Because of the signal from the country code, hreflang tags are not required when utilizing different domains (ccTLDs), yet some individuals choose to use them with the argument that the hreflang tag can reinforce the location signal.
Follow the guidelines below if you chose to utilize hreflang tags. Users of WordPress: You might be able to manage your hreflang tags with a plugin.
How to Make Use of Hreflang Tags
Take into account that overseas information is frequently a translation of English-language pages. This results in a separate version of the same page with a similar URL for each language, which means that these versions may compete in search results. A hreflang tag is added to each version of a URL on your website, which helps to avoid competition.
The hreflang tag might have two parts:
- The language code (using ISO ISO 639-1 code) is required.
- A nation code (using ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country codes) is optional.
A hreflang tag should be formatted as hreflang=”language code-country code.”
Example of Hreflang Tags
By inspecting Apple’s source code, you may see the following hreflang attributes:
Each tag, which is added after the URL, specifies the user’s country and language. “ar-AE” is for Arabic speakers in the United Arab Emirates, “en-AE” is for English speakers in the United Arab Emirates, and so on.
If your main page automatically redirects users based on their location or prompts them to select a language for the page (like in the Air Canada example above), you may additionally require an x-default hreflang tag. This attribute value “signals to our algorithms that this page does not target anyone’s language or location and is the default page when no other page is better suited,” according to Google.
There are three places where you can use hreflang tags:
- In the header source code for each page (most popular)
- On every page, in the HTTP header
- Within your sitemap
Choose the one that is easiest for you to maintain, but make sure that you only use your hreflang tags in one of these places on your site.
Step 4: Provide more signals to international SEO
Localizing material extends beyond the technological options discussed above. International SEO might benefit from a well-rounded understanding of a target country’s or language’s users.
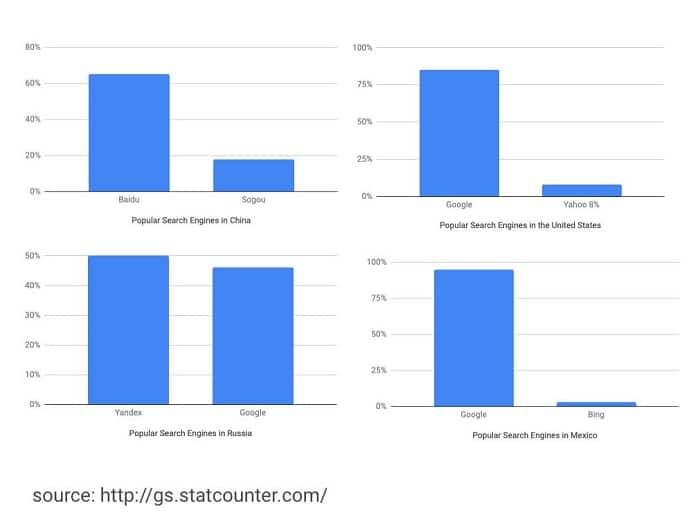
Take into account Search Engine Preferences
Google has the highest proportion of Internet searches, accounting for 92 percent worldwide. However, this is not the case in every country. Baidu, for example, controls 65 percent of the market segment in China. Yandex is well-known in nations throughout Eastern Europe.
While search engines have many commonalities, you should investigate how to improve your foreign SEO efforts for Baidu or Yandex, for example, if China or Eastern European countries are part of your global presence.
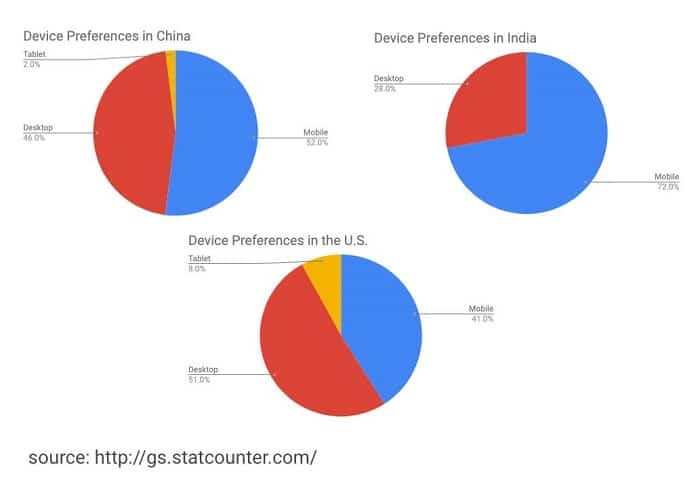
Content should be tailored to the preferences of the device
People in many countries like to access the Internet in various ways. Making your material accessible across the most popular devices can improve usability, which can influence SEO. Knowing how people use search might help you decide where to focus your efforts to improve their experience.
Consider Other Local Signals
Additional geo-targeting cues can help you. Consider using the following ways to indicate your users’ country or language:
- Include links to your social media presence on major local social media platforms.
- Prices are displayed in the currency of the user’s choice.
- Include information on your local offices’ locations, such as their address and phone number.
Because the ultimate goal of your international SEO efforts is to provide excellent service to your clients, it will be worthwhile to learn about local preferences for colors, design aesthetics, content structure, and other cultural considerations. Whenever feasible, ensure that your translated content is created by a native speaker and approved by members of the intended audience.
Begin with International SEO
Understanding how to best serve your clients and then taking steps to personalize your content and search experience to their demands is the first step in international SEO. Using the techniques outlined above, you can begin working on international SEO to optimize your website for viewers in different countries or who speak different languages.
You May also like sitescorechecker, Pro Site Ranker