Google fines can be expensive. Being deleted from search rankings can result in a loss of visitors, visibility, and money. Use this article to learn what Google penalties exist, how to run a penalty check quickly, and how to recover from any penalties you uncover to help safeguard your site from a sudden and extended drop in performance.
What Exactly Is a Google Penalties?
A Google penalty is a disciplinary measure taken by Google against a website when it finds that pages on the site violate webmaster quality rules. If a website obtains a Google penalty, some or all of its pages will be removed from Google search results.
Google penalties are known as manual actions by Google, although many marketers wrongly refer to algorithm upgrades as a form of search penalty.
When a human reviewer at Google determines that one or more pages on a site are not compatible with Google criteria, the site is subjected to manual actions. They are actual search penalties designed to combat attempts to alter Google’s search algorithm through the use of black hat SEO practices.
Algorithm upgrades alter how Google ranks material, which might cause a website’s rating to fall. This was particularly noticeable during upgrades. While sites may lose search exposure as a result of these changes, algorithm upgrades do not constitute site penalties. They only have an effect on search visibility as ranking variables change.
This post will concentrate on Google penalties that may be recognized and fixed manually.
Is My Website Under Google Penalties?
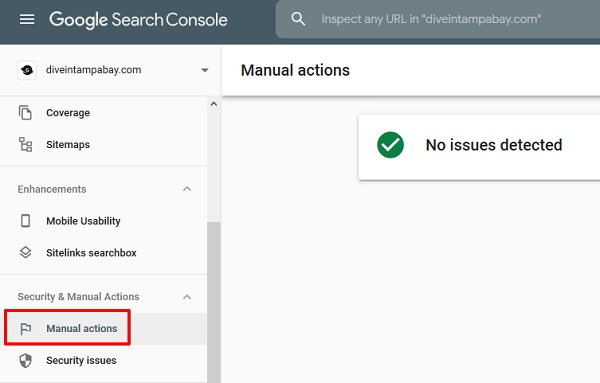
The Google Search Console serves as a penalty checker. View the Manual Actions page in your Google Console account to see whether you have any Google penalties. If you have any fines, they will be posted beside the impacted pages. A green checkmark will appear if you have no Google penalties.
Google Penalties: How Long Do They Last?
A Google manual action penalty can remain as long as you don’t settle it. You may get rid of it by locating the problem, resolving it, and then filing a Review Request via Google’s URL Inspection Tool. Google will notify you of the resolution once they have confirmed that the issue has been resolved.
Read more on Website speed, Small Business seo
11 Google Penalties to Stay Away From
If a penalty check shows that your site has problems, Google has discovered one of the following issues.
1. Links to Your Site That Aren’t Natural
Google discovered a pattern of links connecting to your site that was “unnatural, fake, deceitful, or manipulative.” This Google backlink penalty is frequently applied to websites that purchase links or participate in link schemes. Make sure you understand the many types of backlinks available, including which will benefit your site and which will harm it (or lead to a Google penalty).
2. Your Site’s Unnatural Links
On your website, Google discovered “unnatural, fake, fraudulent, or manipulative” outbound links. The links do not appear to have been included for editorial purposes. Instead, they appear to have been added solely to manipulate search rankings. As previously said, good internal and external linking tactics are crucial for establishing authority and a strong SEO presence. However, if your links are of no value or are used to trick search engines, your site will most likely be penalized.
3. Content that is thin and has little or no added value
Google discovered low-quality or shallow pages on your site. The pages look to be low-quality guest posts, doorway sites, or thin affiliate pages, or they appear to include automatically created or scraped content. Google’s objective is to offer searchers the most valuable, relevant content possible. If your content has no distinctive value, is repeated, or is full of keywords but no meaningful information, you may be subject to this penalty.
4. Stuffing Keywords
Google discovered pages on your website that appear to be keyword stuffed. Pages that use keyword stuffing unnaturally repeat the same target keyword multiple times in order to rank for the phrase. Throughout the page, the keyword is employed awkwardly, out of context, and excessively.
5. Links and Hidden Text
Google discovered misleading language and links on your website. Using white text on a white backdrop, hiding text behind an image, setting the font size to zero, or using CSS to position text off-screen are all examples of this.
6. Cloaking and Deceptive Redirections
Google discovered that your website displays distinct material or URLs to human users and search engines. Sneaky redirects link people to a page that differs from the one displayed to Google. Cloaking-enabled content displays different copies and pictures to human users than to search engines.
7. Clever Mobile Redirections
Google discovered deceptive mobile redirection. Mobile redirects should take viewers to a mobile-friendly version of the original page. Users are sent to a page with content unrelated to the original by sneaky mobile redirects.
8. Incompatibility of AMP Content
Google discovered AMP pages that do not correspond to the original material. AMP pages should, in general, adhere to regular search guidelines. According to additional standards, users should be able to experience the same information and perform the same or similar actions on AMP pages as they do on the original page. The content on mismatched AMP pages differs from the original. The purpose of requiring content consistency between AMP and canonical URLs is to create a seamless and valuable user experience that is free of interruptions and extra processes.
9. The Structured Data Problem
Google discovered structured data, also known as schema markup, that is deceptive or manipulative. The structured data may contain content that is irrelevant or invisible to consumers, or it may violate structured data principles in other ways. A few concrete examples of structured data difficulties are shown below. The whole list and descriptions can be found on Google’s support page.
Structured data is not the same as page content.
Structured data was discovered on hidden content Specific data kinds are in violation of Google guidelines; they are erroneous or deceptive.
10. Spam Created by Users
Google discovered spam on your site that was contributed by users. Comments and links in forums and comment sections are examples of user spam. It could even comprise entire pages of material on websites that allow users to create new pages.
11 – Complete Spam
Google discovered that your website had persistent or serious violations of its quality rules. The site may contain scraped, automatically created, or shallow information on several pages, or it may engage in malevolent activities (such as phishing or installing viruses, trojans, or other badware).
Google Penalties Recovery: How to Repair and Avoid Search Penalties
To detect and fix Google penalties on your site, follow these three steps:
- Use Google Console as a penalty checker to detect problematic pages and the fines associated with them.
- Follow the advised activities in Google’s Manual Action report and the guidelines above to engage in Google penalty recovery.
- Use Google’s URL Inspection Tool to submit a Review Request.
The first step in avoiding Google penalties is to understand what causes them.
Use only white hat SEO approaches and an on-page SEO checker to ensure that your content adheres to SEO best practices.
You May also like sitescorechecker, Pro Site Ranker